前言:
简单记录一下,内存管理函数
为什么使用动态内存呢?
简单理解就是可以最大限度调用内存
用多少生成多少,不用时就释放而静止内存不能释放
动态可避免运行大程序导致内存溢出
C 语言为内存的分配和管理提供了几个函数:
头文件:<stdlib.h>
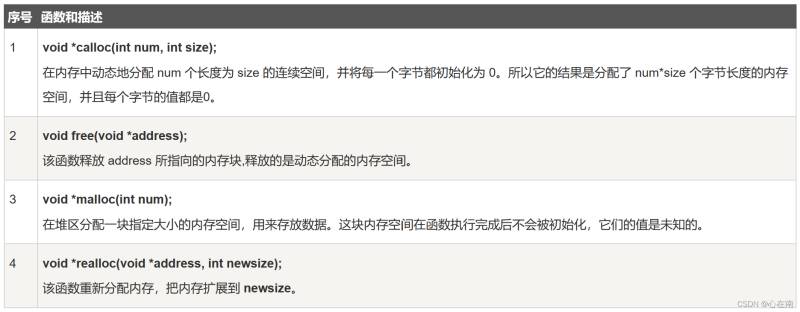
注意:void * 类型表示未确定类型的指针
1.malloc() 用法
分配一块大小为 num 的内存空间
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char name[12];
char *test;
strcpy(name, "KiKiNiNi");
// 动态分配内存
test = (char *) malloc(26 * sizeof(char));
// (void *) malloc(int num) -> num = 26 * sizeof(char)
// void * 表示 未确定类型的指针
// 分配了一块内存空间 大小为 num 存放值是未知的
if (test == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error - unable to allocate required memoryn");
} else {
strcpy(test, "Maybe just like that!");
}
printf("Name = %sn", name);
printf("Test: %sn", test);
return 0;
}
// 运行结果
// Name = KiKiNiNi
// Test: Maybe just like that!
2.calloc() 用法
分配 num 个长度为 size 的连续空间
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char name[12];
char *test;
strcpy(name, "KiKiNiNi");
// 动态分配内存
test = (void *) calloc(26, sizeof(char));
// (void *) calloc(int num, int size) -> num = 26 / size = sizeof(char)
// void * 表示 未确定类型的指针
// 分配了 num 个 大小为 size 的连续空间 存放值初始化为 0
if (test == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error - unable to allocate required memoryn");
} else {
strcpy(test, "Maybe just like that!");
}
printf("Name = %sn", name);
printf("Test: %sn", test);
return 0;
}
// 运行结果
// Name = KiKiNiNi
// Test: Maybe just like that!
3.realloc() 与 free() 用法
重新调整内存的大小和释放内存
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char name[12];
char *test;
strcpy(name, "KiKiNiNi");
// 动态分配内存
test = (char *) malloc(26 * sizeof(char));
// (void *) malloc(int num) -> num = 26 * sizeof(char)
// void * 表示 未确定类型的指针
// 分配了一块内存空间 大小为 num 存放值是未知的
if (test == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error - unable to allocate required memoryn");
} else {
strcpy(test, "Maybe just like that!");
}
/* 假设您想要存储更大的描述信息 */
test = (char *) realloc(test, 100 * sizeof(char));
if (test == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error - unable to allocate required memoryn");
} else {
strcat(test, " It's a habit to love her.");
}
printf("Name = %sn", name);
printf("Test: %sn", test);
// 释放 test 内存空间
free(test);
return 0;
}
// 运行结果
// Name = KiKiNiNi
// Test: Maybe just like that! It's a habit to love her.
到此这篇关于C语言动态内存管理介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C语言动态内存内容请搜索悠悠之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持悠悠之家!
发表评论 取消回复